How Chinese Medicine Understanding Eye Problems ?
- Differentiation of visual problems
- Differentiation of painful eyes
- Differentiation of itchy eyes
- Differentiation of dry or gritty eyes
- Differentiation of light sensitivity of eyes
- Differentiation of blinking of eyelids
- Differentiation of redness and swelling of the eyes
- Differentiation of discharges of eyes
- Differentiation of tearing of eyes
The eyes rely on other body components to function properly. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) views the eyes as part of organic whole of the body; the eyes are closely tied with internal organs, other structures, and tissues through the meridian system. The health of the eyes can influence and be influenced by other parts of the body.
The eyes are sense organ for seeing things and differentiating colors, which need nutrient essence from the internal organs to support and nourish. Through the transmission of the meridians, disturbances of internal organs will affect the eyes correspondingly, even result in eye problems. On the other hand, when the eyes have health problems, it will bring pathological influences towards internal organs, leading to abnormal blood and qi (vital energy) activities, and general body responses. With this holistic view, TCM physicians always consider the interrelationships between the eyes and organs, most eye problems are considered as reflection of the health of the whole body.
- Liver meridian connects to eyes: Leg Jue Yin Liver Meridian starts from the foot and ends on the head. A branch of the meridian runs upward and enter the nasopharynx region, connects with the eyes and then continues upward to emerge from the forehead and ends at the vertex of head. The eyes are nourished by nutrient essence derived from the organs through the delivery of the liver meridian.
- Liver blood and qi flow up to eyes: The liver is responsible for storing and regulating blood flow of the body. Abundant blood and qi in the liver ensures the eyes to get proper nourishment, and so keep a sharp vision of eyes.
- Liver problems often affect eyes: Eyes symptoms are common in liver disorders, for example liver-yin deficiency leads to eye dryness, liver-blood depletion leads to blurry vision or night vision problems, wind heat in liver meridian leads to red, itchy and painful eyes, up-flaring liver fire leads to red and painful eyes, liver yang hyperactivity leads to dizziness and headache, internal stirring of liver wind leads to double vision. In modern diseases such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis or cancer, it is not uncommon for the patients to experience yellow eyes, blurry vision, dry eyes, visual fatigue or double vision; more seriously there may have sensory degeneration of the cornea, retinal bleeding or inflammation.
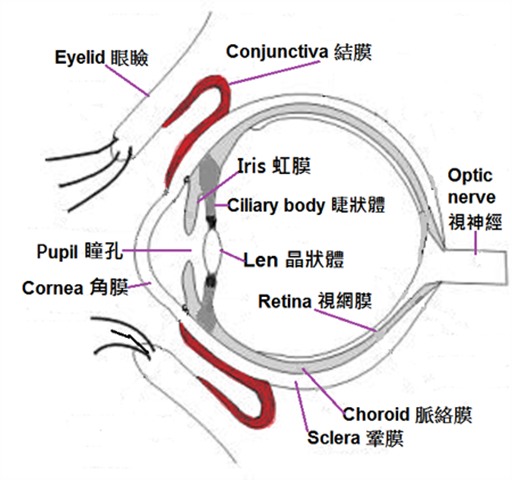
1. Differentiation of visual problems
Visual problems can be originated from inside or outside the eyeballs, it is important to identify that firstly.
- Blurry vision accompanied with bloodshot and burning eyes or cloudy eyes indicate externally contracted of wind heat or blazing fire in liver and gallbladder.
- Blurry vision and dim vision gradually can be due to liver and kidney deficiency, or yin deficiency with flaming fire, or liver qi stagnation.
- Eye floaters tends to indicate turbid phlegm disturbing eyes, or yin deficiency with flaming fire, or deficiency of liver and kidney.
- Blurry vision while moving the head or standing up suddenly usually indicates depletion of blood and essence.
- A sudden reduced in vision alone may indicate bleeding due to blood heat, or liver fire disturbing eyes, or yin deficiency with flaming fire, or deficiency of liver and kidney.
- Long-lasting cataracts that have interrupted vision or even caused blindness, individuals usually accompany depletion of qi and blood, or deficiency of liver and kidney.
- Night vision problem with a narrowed visual field usually indicates essence depletion of liver and kidney, or yang deficiency of spleen and kidney.
- Short-sightedness (myopia) may be due to yang qi depletion or intense use of eyes.
- Far-sightedness (hyperopia) may be due to depletion of yin essence.
- Visual distortions may be due to yin deficiency with flaming fire, depletion of essence and blood, blood stasis and qi stagnation, turbid-dampness disturbing eyes.
2. Differentiation of painful eyes
Painful eyes are common, it can be originated from outside or inside the eyeballs. It is a routine to identify the nature of pain and disharmony pattern first. For example, excess patterns tend to present as violent pain, persistent pain, swollen pain, hot pain, pain aggravated by pressing, and pain accompany with irritability; while deficient patterns tend to present as chronic pain, intermittent pain, dull pain without swelling, cold pain, pain alleviated by pressing. Pain occurs between midnight to noon belongs to yang pattern; pain occurs between noon to midnight belongs to yin pattern.
- Pain alleviated by warming belongs to a heat sign, pain alleviated by cooling belongs to a cold sign.
- External eye pain such as gritty pain, burning pain, pain with a feeling of something in eye, and sharp pain tend to be yang pattern.
- Internal eye pain such as distending pain, dragging pain, and deep pain tend to be yin pattern.
- Gritty pain or burning pain with red eyes, sticky and excess eye discharge tend to indicate externally contracted wind and heat.
- Burning pain with swollen hard eyelid, and also constipation or dry stools tend to indicate excess fire in Yang Ming.
- Dry and gritty feeling with mild bloodshot eyes tend to indicate blood deficiency and fluid depletion.
- Distending pain with hardened eyeball tends to indicate adverse up-flowing of fire, and obstructed blood and qi flowing.
- Dull and distending eye pain tends to indicate insufficiency of yin essence, and hyperactive yang in the head.
- Distending feeling while focusing tends to indicate insufficiency of spleen and kidney (essence failing to nourish the eyes), or a sign of hyperactive yang.
- A deep pain in eye region tends to indicate liver qi stagnation, or yin deficiency with flaming fire.
- Eye pain that radiates to the vertex of head and the back of neck indicates evils attacking Tai Yang Meridian; eye pain that radiates to the temple area of head indicates evils attacking Shao Yang Meridian; eye pain that radiates to the forehead, nose and teeth indicates evils attacking Yang Ming Meridian.
3. Differentiation of itchy eyes
- Itchy and red eyes that aggravated by wind blowing tend to indicate externally contracted with wind heat.
- Severe eyelid itching with marginal ulcers or nodules glowing in inner surface tend to indicate damp-heat in spleen and stomach, in combination with irritation of wind evils.
- Itchy and painful eyes with severe burning and swelling tend to indicate extreme flaming of toxic wind and heat.
- Intermittent gritty and itchy eyes tend to indicate blood deficiency generating wind.
4. Differentiation of dry or gritty eyes
- Dry and scratchy feeling in the eyes tend to indicate depletion of body fluids, or depletion of both fluid and blood.
- Gritty and scratchy eyes like there’s something in the eyes may be due to trachoma, an infectious disease.
- Gritty eyes accompany with redness, itching, burning pain, sensitive to light, lots of tear may be due to wind heat irritating eye, blazing fire in liver and lung, and also foreign objects in the eye socket.
5. Differentiation of light sensitivity of eyes
Light sensitivity is a symptom with bright lights hurt the eyes, also known as photophobia.
- Sensitive to light accompany with red, swelling, itchy, painful and teary eyes usually associated with wind heat or liver fire.
- Sensitive to light with dry eyes only usually caused by yin deficiency and blood insufficiency.
6. Differentiation of blinking of eyelids
- In sick kids, frequent blinking that prefers rubbing eyes tend to indicate spleen deficiency and liver heat. The kid may have digestive and absorption problem, a thin physique and be a picky eater.
- Uncontrolled frequent blinking with dry eyes, and also throat and mouth dryness tend to indicate yin deficiency of lung.
- Uncontrolled frequent blinking can also appear in wind heat irritating eye problems, or nearsightedness.
7. Differentiation of redness and swelling of the eyes
- Eyelids become red and puffy, with burning pain or hardening or pus forming tend to indicate toxic-heat accumulating in spleen and stomach, or heat and stasis in blood system.
- Sudden eyelid swelling with mild redness, burning and tearing tend to indicate external wind irritating.
- Generalized puffy eyelids that are soft and tightened skin surface, and without redness and pain tend to indicate yang deficiency of spleen and kidney (water flooding in the head).
- Red swelling eyelids with ulcers tend to indicate damp-heat steaming.
- Purplish swelling eyelids tend to indicate blood stasis and qi stagnation.
- Sudden pink eyes with clear tearing tends to indicate externally contracted wind and coldness.
- Sudden bloodshot and painful eyes, with excess tear and discharge tend to indicate externally contracted wind and heat.
- Bright red area in the white of eyes indicates excess heat in lung meridian, or excess heat in triple burner.
- Swelling and purplish-red conjunctiva (white of eye) indicates toxic heat accumulation.
- Bright red ring around the cornea, feeling burning and light sensitivity and tearing indicate excess heat in liver and gallbladder.
- Mild red ring around the cornea, with blurry vision and tearing indicate yin deficiency with flaming fire.
8. Differentiation of eye discharges
- Excess hard discharge of the eyes indicates excess heat in lung meridian.
- Thin and soft discharge of the eyes indicates virtual heat in lung meridian.
- Excess thick and yellow-greenish discharge of the eyes indicates toxic heat flaming.
- Sticky discharge of the eyes often indicates damp-heat.
- For patients with measles, excess discharge of the eyes indicates either wind-heat attacking, or excess fire in heart and lung.
9. Differentiation of tearing of eyes
- Excess tearing with a warm feeling, accompany with redness, swelling, burning and light sensitivity of the eyes often indicate excess fire in liver and gallbladder, or wind heat in liver meridian.
- Intermittent tearing that aggravated by wind blowing, and without redness and swelling, often indicate deficiency of liver and kidney that fails to control tearing, or the tear ducts are blocked.
- Intermittent tearing that can squeeze out sticky or pus discharge when pressing the inner eye corner, often indicate heat accumulated in heart meridian.
- A declined in tear amount, dry eyes and blurry vision can be resulted from flaming up of virtual fire, under-nourished eyes or other eye structural damages.
- For sick kids, crying with tear may indicate a mild condition, while crying without tear may indicate a severe condition.