What Are The Yin Yang Organs ?
 In western medicine, the body's organs are explained in terms of their anatomical structures and physiological functions. However, in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the approach is quite different. Ancient Chinese studied internal organs through direct observation on the external body, organs are considered functional units of the body. Therefore, what is typically thought of as an organ i.e. heart, liver, stomach etc. has a much broader meaning and application in TCM. An organ's anatomical structure is not as important as its functional properties or relationships with other organs.
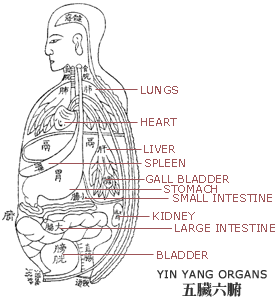
In western medicine, the body's organs are explained in terms of their anatomical structures and physiological functions. However, in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the approach is quite different. Ancient Chinese studied internal organs through direct observation on the external body, organs are considered functional units of the body. Therefore, what is typically thought of as an organ i.e. heart, liver, stomach etc. has a much broader meaning and application in TCM. An organ's anatomical structure is not as important as its functional properties or relationships with other organs. According to the functions of internal organs, Chinese medicine recognizes five yin organs and six yang organs, known as "zang" and "fu" organs respectively, and also some extraordinary organs.
The yin organs include the liver, heart, spleen, lung and kidney. The pericardium is sometimes considered a sixth yin organ. The function of the yin organs is mainly for producing, transforming, regulating and storage essential substances. In general, yin organs do not have empty cavities.
The six yang organs are made up of the gall bladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, bladder and triple burner. The triple burner does not have a physical structure and is considered a functional unit. The yang organs are mainly responsible for digesting food and transmitting nutrients to the body and also excretions. Usually, yang organs are organs with empty cavities.
The extraordinary organs include brain, bone, marrow, blood vessel and uterus. Since the functions or structures of these organs cannot be classified according to the yin or yang orangs, and thus they are regarded as the extraordinary organs.
Relationships between the Yin and Yang Organs
TCM views the body as an organic whole, in which the liver, heart, spleen, lung and kidney are acted as the cord functional units. With the help of meridian system, the five organs link up other parts like six yang organs, body tissues, orifices, and brain, and form a complex set of interrelationships within the body. Every part of the body as well as their activities correspond to one of the five organs, and the five organs themselves are interrelated too. The functions of the body are largely based on harmonious relationships between the five organs. Based on the way of meridian connections, one yin organ and one yang organ can be further paired, known as an interior and exterior relationship. This special relationship makes the two organs more related in physiology and pathology. It is generally stated that the interior belongs to yin and the exterior belongs to yang. Yin organs are thought to have more internal functions and are called interior organs. They play a more important role in TCM medical theory and practice. The yang organs, on the other hand, are believed to have more external functions and are considered exterior organs.
| Yin organs (interior organs) | Yang organs (exterior organs) |
| Liver | Gall bladder |
| Heart | Small intestine |
| Spleen | Stomach |
| Lung | Large intestine |
| Kidney | Bladder |
| Pericardium | Triple Burner |