Missed Period Overview
 Missed period can occur before puberty, during pregnancy and lactation, or after menopause, these are normal physiological signs. Amenorrhea is a medical term for missed period, a menstrual disorder due to certain health conditions.
Missed period can occur before puberty, during pregnancy and lactation, or after menopause, these are normal physiological signs. Amenorrhea is a medical term for missed period, a menstrual disorder due to certain health conditions. If missed period happen in the reproductive age, pregnancy should always be ruled out before considering a menstrual disorder, then the challenge is finding the underlying cause for the absent periods.
Missed period can either be primary or secondary. Primary missed period is when periods do not start during puberty; secondary missed period is an unexpected cessation of the menstrual cycle.
Normal menstrual cycles rely on a complex feedback system between the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the ovaries, and the cyclical reaction of the lining in the uterus to sex hormones, see graphic below:
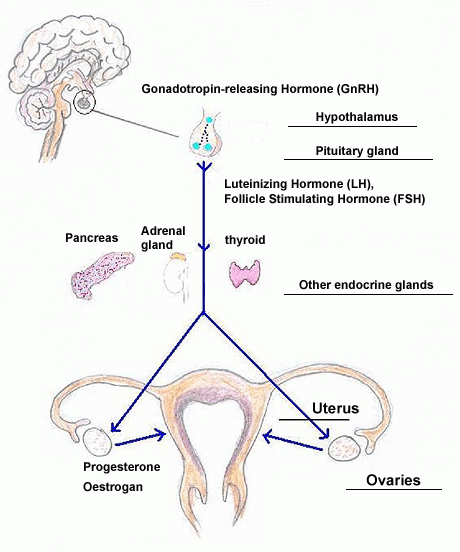
From the above, it is clearly showed that the endocrine system plays a major role in the development of menstrual disorders, and thus doctors usually prescribing hormone therapy to regulate menstrual cycles.
Possible causes of missed period
Missed period is just a symptom, the underling problem can arise from multiple factors, and even complex situations sometimes, including inborn defect, underdevelopment, endocrine problems, immune disorders, emotional distress, tumors, injuries as well as medication effects.- Abnormalities in the uterine lining, such as birth defects, infections and poor response to hormones;
- Ovarian dysfunction, such as premature ovarian failure and tumors;
- Pituitary dysfunction due to factors like tumors and postnatal injuries;
- Hypothalamus dysfunction that usually resulted form mental stress, severe malnutrition and taking birth-control pills.
- Other endocrine disorders arising from the adrenal glands, thyroid or pancreas.
Besides missed period, individuals can have various presentations. For example, individuals with a hormone disturbance may have excessive body and facial hair, acne, unusual breast secretions, dry skin, sensitivity to cold temperatures, a change in voice or sex drive, weight gain, or weight loss.
You should consult a gynecologist if your first menses have not come by age sixteen. For secondary cases, if missed period are not due to physiological factors such as pregnancy or menopause, and last for more than three cycles, you should also seek medical advice.
During a consultation, the gynecologist will obtain a detailed history and perform physical examination. Investigations like blood tests, x-rays, ultrasound scans, as well as chromosome testing may also be necessary. The following are frequently asked in the first visit:
- The last menstrual period date
- The pattern of your menstrual cycles
- Whether you are sexually active
- Pregnancy history
- Birth control method
- Eating habits
- Emotional state
- Exercise program
- Current medication
Missed period is rarely caused by a life-threatening condition. In most secondary cases, the underlying problems are reversible and treatable; routine treatments include oral supplemental hormones, surgery or simply a change in lifestyle.