Fructus Psoraleae
- Name
- Origin
- Where Does It Grow?
- Nature and Flavor
- Identified Active Components / Major Chemical Constituents
- Drug Actions in TCM

- Traditional Uses in TCM
- Pharmacological Actions
- Toxicology
- Administration and Dosage
- Adverse Effect, Side Effects and Cautions
- References
Name
Latin Name: Fructus Psoraleae
Common Name: Psoralea
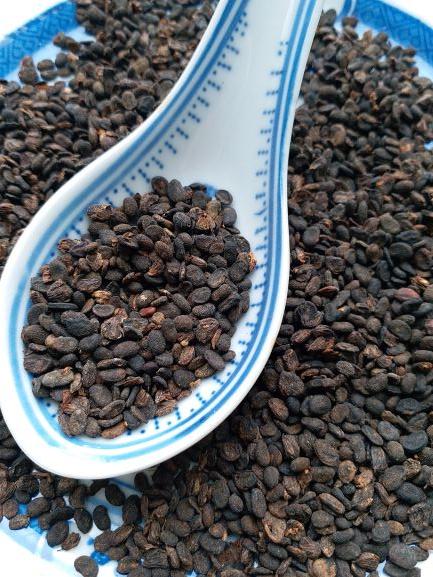

Scientific Name: Psoralea corylifolia L.
Chinese Name: 補骨脂
Pinyin Name: bu gu zhi
Origin
The ripe fruit of Psoralea corylifolia L., an annual herbal plant of the Leguminosa family.1
Where Does It Grow?
Psoralea is mainly produced in Shaanxi, Henan, Sichuan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Shanxi, Guangdong, Guizhou, Yunnan and Shanxi provinces of China.1
Nature and Flavor
Psoralea is pungent and bitter in flavor, warm in nature; and mainly manifests its therapeutic actions in the kidney and spleen meridians.1
Identified Active Components / Major Chemical Constituents
- Volatile oils include limonene, terpin-4-ol, linalool, β-caryophyllene and geranyl acetate.6-8
- Coumarin derivatives include psoralen, isopsoralen, psoralidin, isopsoralidin, corylidin, bavacoumestan A, bavacoumestan, B sophoracoumestan A and 8-methoxypsoralen.
- Flavones include coryfolin, corylifolinin, bavachinin, isobavachin, neobavaisoflavne, bavachromene, corylin, bavachalcone and neobavachalcone.
- Mono-terpane-phenol includes bakuchiol.
- Lipids include triglycerides, diglycerides and monoglycerides.
Drug Actions in TCM
Psoralea invigorates kidney, supports yang, consolidates essence, reduces excessssive urination, warms spleen, stops diarrhea, supports the grasping of qi and relieves asthmatic symptoms. 1 Traditional Uses in TCM
Pharmacological Actions
Animal studies
2. Anti-cancer Effect
Animal studies
Animal studies
Clinical observations
Clinical observations
When 0.2ml of Fructus Psoraleae was directly injected into 163 cases of people with corns (a painful, cone-shaped, overgrowth and hardening of the epidermiswith the point of the cone in the deeper layers. It is produced byfriction or pressure.), the successful treatment rate after one single injection was reported to be 84%.17
Toxicology
Administration and Dosage
For decoction, the usual dose of psoralea is 6~15g.1
Adverse Effect, Side Effects and Cautions
Psoralea is not suggested for those have yin vacuity with internal heat, chronic kidney problems, skin rashes caused by abnormal immune functions, infertility or habitial abortion in women.3
References
- Lui Daiquan, ed. Chinese Medicine. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2000-6.
- Li Jiashi, ed. Chinese Medicine Identification. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2000-6.
- Wu Yiluo. Bencao Congxin (New Compilation of Materia Medica), 1757AD.
- Li Shizhen, Bencao Gangmu (Compendium of Materia Medica) 1578AD.
- Jiangsu Medical College, Pharmacopoeia of Chinese medicine (The First Volume), Shanghai People Hygiene Publisher, Shanghai, China 1997;2006.
- Yang Yishan, et al. Experimental study of the anti-cancer effects of six Chinese Medicine preparations, Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Chinese Material Medica of Shanxi 1983;12(10):49.
- Zhao Jianbin, et al. The killing effects of Fructus Psoraleae and radiation on Sarcoma cells, Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Shanxi 1990;11(9):427.
- Lu Zehua, et al. The in-vitro observation of the killing effects of Fructus Psoraleae on human leukemic cells, Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 1987;7(12):736.
- Wang Yusheng, ed. The application and pharmacology of Chinese Medicine 1st edition, Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1983:547.
- Hua Shizuo, Treatment of leucopenia with Fructus Psoraleae, Modern Meicine, 1975:6(10):497.
- Zhang Yongsheng, et al. The experimental study of the effects of isomeric structure of psoralen and black light on human lymphocytes, Journal of Dermatology of China 1983:16(2):106
- Ma Rou, et al. The effects of paired and single ingredient Chinese Medicine on the hematopoietic cells, Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 1984:4(9):533
- Sun Yan, et al. The cancer treatment effects of the principle of normal qi support in Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine, Journal of Medicine of China 1981:61(2):97
- Zhao Jiying, et al. Common wart treatment with ethanol extract of Fructus Psoraleae, Journal of Dermatology of China 1989:22(2):116
- Lu Yongtian, et al. Observation of 800 cases of Psoriasis treatment efficacy with Fructus Psoraleae injection, Journal of Chinese Medicine 1982:23(9):31
- Wei Jicheng, et al. Clinical trial of treatment common Psoriasis with 8-methoxypsoralen in combination with black light radiation, Chinese Herbal Medicine 1980:11(5):212
- Guo Chaoguang, Observation of corn treatment efficacy with local injection of Fructus Psoraleae ethanol extract, Newsletter of Chinese Herbal Medicine 1978:9(8):34
- Xu Jianguo, Effects of Fructus Psoraleae on tyrosinase activation, Chinese Herbal Medicine 1991:22(4):169
- Zhou Jinhuang, Pharmacology of Chinese Medicine, 1st version, Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers 1986:257
- Quoted in "Wang BX ed. Modern Pharmacological studies on Chinese Medicine. Tianjin Scientific Technology Publishing, 1999: 1248-1250"