Sweating Problems in Chinese Medicine
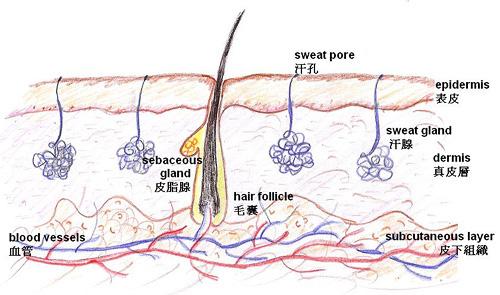
Sweat glands of the skin Over 1% of the world's population suffers from excessive sweating, medically known as hyperhidrosis. Other than for hot weather, exercise or emotional reasons, these individuals tend to sweat excessively without a trigger. Excessive focal sweating such as on the face, hands, feet or underarms usually has no apparent cause; the condition seems to run in families. However, excessive sweating over a large area of the body may indicate an underlying cause. It can be a side effect of medication or a sign of health problems commonly seen in menopause, low blood sugar, hyperthyroidism, anxiety, cancer and infections. Therefore, the treatment of abnormal sweating should be according to the underlying health problems. You should seek professional help if you experiencing the followings:
- The sweating disrupts your daily routine;
- Suddenly sweating much more than usual or if the sweating lasts a long time without any obvious reason; Sweating occurs mostly during sleep;
- Sweating accompanied with weight loss, chest pain or tightness, palpitations, dizziness, lack of appetite, fever or cold clammy hands;
- A change in body odor.
Normal sweating helps regulate and harmonize the internal and external body, and is also responsible for nourishing the skin. Sweating has a dual nature when occurring in disease; the first is to eliminate pathogens, a normal reaction of the body’s defense system. Secondly, as sweat is transformed from body fluids, excessive sweating depletes body fluids and blood causing further internal disturbance. Therefore enquiring about sweat is an important part of clinical consultation for physicians. This chapter is about how TCM understands and diagnoses abnormal sweating conditions:
- TCM views on the development of excessive sweating
- TCM diagnostic criteria of abnormal sweating
- Treating focal sweating problems by Chinese methods
- Main references