The ears are complex yet delicate structures responsible for both hearing and balance. Ear ringing, also known as tinnitus, can develop gradually over time or appear suddenly. Researchers are still not entirely sure how this symptom arises. However, many factors that can trigger or worsen tinnitus have been identified. Here are some questions that might help you find the possible causes:

Exposed to loud noises?
Loud noise is the leading cause in ear ringing, especially for those who listen to loud music, or work with chainsaws, guns, and other noisy devices. Ear ringing is a warning sign that indicates the noise around is too loud. It may appear in one or both ears, either permanent or temporary. Individuals may have hearing loss and pain too.
Blockage or infection along the ear channels?
Ear infection causes congestion (pressure buildup) inside the ear, which in turn leads to ear ringing. Sometimes, ringing in the ears may be due to earwax buildup or foreign objects stuck in the ear.
Old enough to have ear ringing?
People of all ages can have ear ringing, but it is more common in those over 60. This is a natural aging process that causes functional deterioration of the inner ear.
Feeling stressful or anxious?
Poor sleep, fatigue, or mental distress such as tension, anxiety, depression can disturb the balance of the inner ear, which makes ear ringing worse.

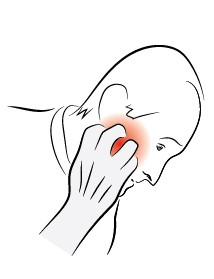
Have a jaw or sinus problem?
Jaw or sinus inflammation may affect the tissues around the ear, leading to hearing problems.
Have a neck or head injury?
For those with neck or head injuries, the way that their brain processes sound may be changed, or they may involve auditory nerve damage, which can result in ear ringing or hearing loss. The injuries can also lead to headaches and memory issues.
Have other health issues?
Many health conditions, such as Meniere’s disease, migraines, anemia,
hypertension, thyroid diseases, circulatory problems, allergies, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, neural disorders, brain tumors, and malnutrition, are linked to ear ringing. Therefore, you should be attentive to any accompanying signs or symptoms that might help identify these conditions.
Taking any medication?
Ear ringing is a common side effect of many medications, as they can damage the auditory nerve and lead to this symptom. Some common medications that may cause tinnitus include several types of antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, hypertension pills, antidepressants, and birth control pills. About 200 prescription and nonprescription drugs list ear ringing as a potential side effect. Please review your medication list with your doctor to see if any of them could be the cause. Your doctor can modify your prescriptions to help alleviate the symptom. Never stop taking a medication on your own without consulting your doctor.
It should be noted that not everyone can easily identify the cause of their ear ringing. This condition can arise from a variety of underlying issues. While some individuals may trace their symptoms back to specific events or health conditions, others may struggle to pinpoint the exact cause. Professional consultation is often necessary to explore potential treatments and coping strategies.