Radix Puerariae
- Name
- Origin
- Where Does It Grow?
- Nature and Flavor
- Identified Active Components / Major Chemical Constituents
- Drug Actions in TCM
- Traditional Uses in TCM
- Pharmacological Actions
- Toxicology
- Administration and Dosage
- Adverse Effect, Side Effects and Cautions
- References
Name
Latin Name: Radix Puerariae
Common Name: Kudzu root

Scientific Name: Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi / Pueraria thomsonii Benth.
Chinese Name: 葛根
Pinyin Name: ge gen
Origin
The dry root of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi / Pueraria thomsonii Benth., a perennial deciduous vine of the Leguminosae family. The cane, leaf, flower bud and seed are also used medicinally. 1,2
Where Does It Grow?
Kudzu root is widely produced in China. Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi is mainly produced from provinces like Hunan, Henan, Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Sichuan. Pueraria thomsonii Benth. is mainly cultivated from Guangxi and Guangdong, other districts like Sichuan and Yunan also cultivated.1,2
Nature and Flavor
Kudzu root is cool in nature, sweet and pungent in flavor, and mainly manifests its therapeutic actions in the spleen, stomach, lung and bladder meridians.3,6
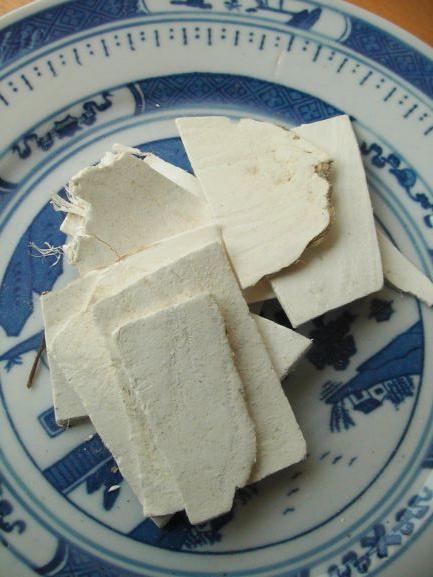
Identified Active Components / Major Chemical Constituents

Drug Actions in TCM
Kudzu root expels pathogens from muscles and skin, reduces fever, promotes fluid production, quenches thirst, promotes eruption and circulation in the meridians and collaterals, and also alleviates hangover.3,6Traditional Uses in TCM
Pharmacological Actions
Toxicology
Puerarin via intravenous injection to rat, the LD50 was found to be 738.1mg/kg or 1g/kg. The maximal dose of puerarin (172.2 mg/kg) to rat via intraperitoneal injection, and the maximal dose of puerarin (91.3mg/kg) to rabbit via intravenous injection, for 14 consecutive days, nothing abnormal was found in the behavior, blood pictures, biology and organ structures. The results indicate that kudzu root has minimal toxicity.5
Administration and Dosage
Taking orally, the usual dosage for kudzu root is 9〜15g, or can be higher to 15〜30g. It is recommended to use dried herb for the purposes of reducing fever and promoting fluid production, while for the purposes of stop diarrhea, the herb has to be processed.3,5
Adverse Effect, Side Effects and Cautions
References
- Li Jiashi (editor-in-chief), Chinese Medicine Identification, Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2000-2.
- Jiang Su New Chinese Medicine College (edited), Chinese Medicine Encyclopaedia, Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2005-5.
- Lui Daiquan (editor-in-chief), Chinese Herbal Medicine, Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2000-6.
- Tao Yufeng, Clinical Herbal Medicine, People's Medical Publishing House, 2005-5.
- Chen Pian, Clinical Application of Tonifying Herbs, Second Military Medical University Press, 2008-8.
- http://www.zysj.com.cn/zhongyaocai/yaocai_f/fuling.html